From simple to nuclear.

Actually, I talk about browser problems all the time. Particularly since people encounter browser problems all the time. 
The problem is that it’s never as simple as telling you, “Well, here’s what you do to stop ‘not responding’ problems.” There are so many possible causes there’s no way to know which one applies to your situation.
What I use instead is a more general approach to dealing with internet web browser problems that applies to all popular browsers — not only FireFox but Chrome, Edge, and others.

Browser problems
Browser issues can be caused by many things, not always the browser itself. To troubleshoot:
- Scan for malware.
- Clear the cache.
- Test with extensions disabled.
- Review security software settings.
- Reinstall the browser.
- Consider switching to a different browser.
These steps apply broadly to all popular browsers. Let’s look at each.
Scan for malware
Browser problems can be a sign of malware, though it’s certainly not the most common cause.
Start by making sure your security tools are up to date; then run full scans. If malware is found, make sure it’s cleaned off.
If that makes your browser problems go away, then you’re done.
Help keep it going by becoming a Patron.
Clear the cache
This is such a common answer that until recently1 I had a stock answer configured in the Ask Leo! question-answering system used by my assistants and myself. A couple of keystrokes on our part provided this answer:
I’ll suggest that you begin by clearing your browser cache as described in this article: What’s a Browser Cache, How Do I “Clear” It, and Why Would I Want To? Sometimes a browser’s cache can become corrupt or confused and can cause a variety of issues.
That answer is so common and so applicable in so many situations that we just got tired of typing it over and over as questions came in.
Needless to say, next to scanning for malware, clearing the cache is the first thing I recommend when dealing with just about any browser-related problem. It clears up a surprising number of issues. Visit What’s a Browser Cache, How Do I “Clear” It, and Why Would I Want To? for instructions.
Disable add-ons
The next recommendation when dealing with browser problems is to disable add-ons or extensions.
Add-ons are software added to your web browser to provide more functionality. Adobe Flash is one example; the LastPass password manager is another. The issue is that add-ons integrate tightly with the browser, and problems caused by a misbehaving add-on can manifest as a browser problem.
In Microsoft Edge, click on the ellipsis and then Extensions in the resulting menu.
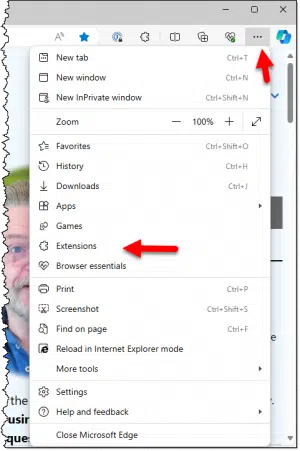
You can also click on the “puzzle piece” icon — — in the toolbar if it’s visible.
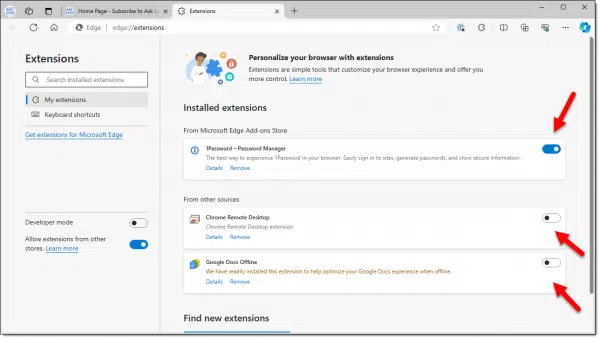
You can turn off individual extensions without removing them.
Start by disabling all of them, and see if your problem goes away. Return to using your browser in whatever scenario was causing issues. If the problem doesn’t recur, then you know that one of the disabled items was the cause. You can then re-enable the add-ons one at a time, returning to using your browser each time, to see which one is responsible for your browser problems.
Other browsers, including Firefox and Chrome, all have a way to manage extensions via either the settings menu or a puzzle-piece icon in the toolbar.
Disable security software
One source of browser problems many people don’t think of is their security software.
Some security packages insert themselves into the activity of your web browser to protect against malicious links, content, and downloads. Many do so in the form of add-ons, which you’ll have seen above. Others, however, use different techniques that aren’t as readily apparent.
I do not recommend uninstalling your security software to diagnose this type of problem.
Instead, I suggest examining your security software for options relating to its interaction with your browser. Unfortunately, different software packages have different terms in different places, but these are the types of options and common phrases you should look for:
- Real-time scanning
- Browser protection or integration
- Download scanning
- Web or URL filtering
There may be others, but the options all focus on what’s being displayed or downloaded by your web browser, typically in real time (i.e., “as it happens”).
Turn all those options off — not permanently, but as a test. If the problems you’re experiencing go away, you’ll know your security software is to blame or at least heavily involved. If there are multiple options, turn them on one at a time to see if you can identify which is the culprit.
Once you understand which option in your security software might be responsible for your browser problems, you can decide between several options:
- Live with the problem
- Disable the option in the security software permanently
- Try different security software
Trying a different browser is also an option I’ll talk about in a moment.
Reinstall the browser
Sometimes the best solution is to start over. By that, I mean:
- Completely uninstall the browser.
- Download the most recent version of it.
- Install that download.
Reinstalling software from scratch is a way to restore any files, settings, or what-have-you that may have been damaged (or confused a little) in the previous setup. It can also eliminate add-ons or even malware you might not even know you have.
Use a different browser
Finally, sometimes the most practical solution is a complete change.
Having problems with FireFox? Try switching to Chrome — or Edge, Brave, Opera, Vivaldi, or any number of alternative browsers available today.
You get the idea. See if using another browser gives you a better experience.
While finding and fixing the problem in the browser you’re used to might be preferable, sometimes the quickest and most pragmatic solution is to try something different.
Do this
When you encounter a problem relating to your web browser, follow the steps above. They apply to all browsers and stand a good chance of helping you resolve whatever issue you’re facing.
If I’ve helped and you’ve fixed it, subscribe to Confident Computing! Less frustration and more confidence, solutions, answers, and tips in your inbox every week.






I don’t know if you include a VPN with security software, but I didn’t find “vpn” on the page. I have to pause my VPN sometimes, and I have it set to bypass some sites.
We still have a stock answer to browser problems and it says the first thing to try is to clear the browser cache. It solves probably over 90% of browser problems.
For years I had an issue with Firefox (and sometimes Chrome) memory usage on a particular news website. RAM would sometimes go as high as 4GB+ and had to force browser shutdown. Cleared cache and tried disabling various extensions with minimal results. Then one day saw a negative review of the AdBlock+ extension. Switched to uBlock Origin. Problem solved.
If you intend to uninstall and reinstall your browser, remember that after you uninstall your browser, you won’t have any way to download the new browser (unless 1: you have multiple browsers installed, or 2) you intend to use Edge to download the installation file). So, before uninstalling, download the installation file for your re-install and save it. Then, uninstall. After you uninstall, you simply run your previously saved installation file.
I mention Edge, because if you are like me, you’ve never used Edge you may be unfamiliar with how to download and save files with it. And, as far as I know, Edge is not easily uninstalled.
As the old joke goes: Edge is a great browser for downloading Firefox. But seriously, Edge is a fine browser, as good as the other popular browsers.
Edge Redeemed
As for how to download files on Edge, it’s similar in all browsers. Click the downloads arrow to view and manage the downloads.

All I can add is, Firefox is the fastest browser on my 2 PC’s.
This wasn’t helpful
Not even close
Not know jargon doesn’t mean we aren’t intelligent
Sorry. One way to learn, however, is by asking questions. For example what “jargon” caused you problems? You can always ask for clarification. That’s one reason comments are here.