And is it something you should worry about?
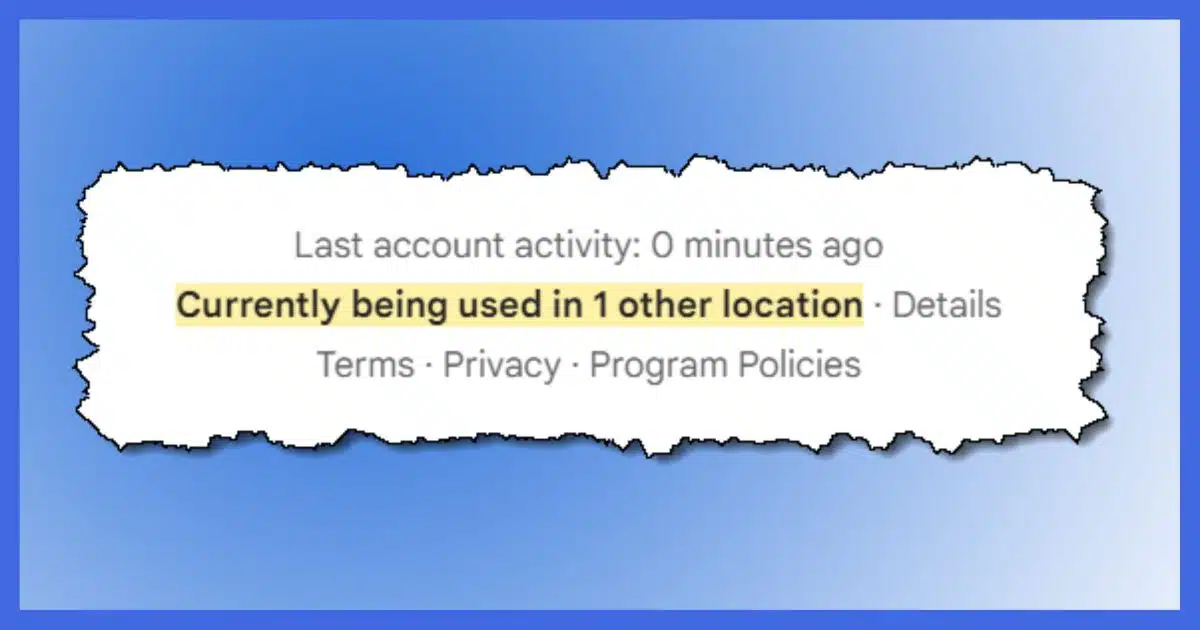
If you ever sign in to Google Mail (aka Gmail) on the web, near the bottom or bottom-right you’ll see a small item: “Last account activity”. It may include a highlighted item: “Currently being used in X other location(s)”.
“Last activity” makes sense, but other locations? Is this something to worry about?
Usually not. But sometimes, maybe. Let’s dive deeper.

Last account activity
Click the “Last account activity” link at the bottom of Gmail’s web interface for information about recent account sign-ins. You can get more detailed information about currently open account sessions, including where (roughly) they are being accessed. If it’s something you don’t recognize, sign out of the offending session and change your password.
Details tell all
Click on the Details link for more information.
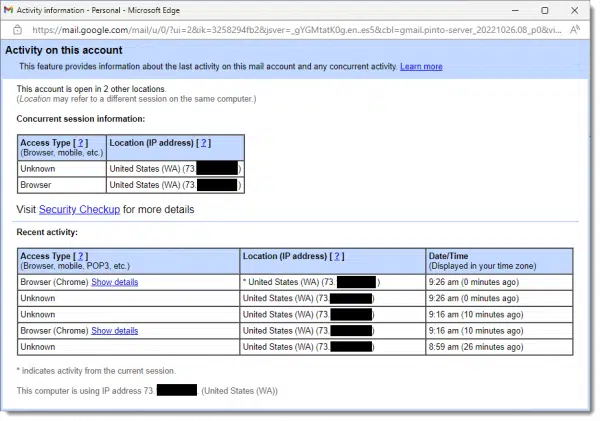
There are two sections: concurrent session information on top, and recent activity below.
Concurrent session information
This section shows the IP address and access type (if known) of all currently active sessions accessing this Gmail account. In the example above, there are two sessions happening at the same time on different… well, this page doesn’t tell us. The IP addresses here are all the same — my home IP address — yet there are multiple active sessions. The key is the line above the information:
Location may refer to a different session on the same computer.
That’s exactly what’s happening here. I have two sessions being accessed from two virtual machines on the same computer:
- Windows 10, accessing the account via gmail.com using Google Chrome
- Windows 11, accessing the account via gmail.com using Microsoft Edge
When you see multiple concurrent sessions at the same IP address, it can be any of the following situations, all accessing the same account:
- Multiple virtual machines
- Different browsers on a single machine
- Different machines connected to the same router, sharing the internet IP address
- Additional software, such as an installed email program like Windows Mail or Microsoft Office Outlook.
- Different devices (i.e., PC versus mobile phone) connected to the same router.
From Google’s perspective, it’s all different activity, even though it’s being accessed via a single IP address.
Recent activity
The Recent Activity section is exactly that: a list of access activity on the account.
Once again, in my case, all the IP addresses are the same, because I’ve only accessed the account from one location.
Note that there are several entries, even though I’ve accessed the account from only two browsers. Closing your browser and re-opening it, or possibly returning to the browser after some idle time, can count as “new” activity, even though it’s technically the same activity as was already listed.
When the IP addresses differ
In the example above, all the IP addresses listed were the same. This is common, and reflects that the account was being accessed from a single location, albeit via different machines and browsers.
But what if the IP addresses differ?
Do. Not. Panic.
The single most common cause is this situation:
- You have one or more devices connected via your home or business internet connection on one IP address.
- You have additional devices connected via your mobile phone provider on a different IP address.
It’s nothing to worry about.
When to worry and what to do
Worry when one of the IP addresses listed is not in your country or you have no other explanation for it. There may be a legitimate explanation, but better to investigate further to be safe.
- Click on the Security Checkup link present in the details window.
- On the resulting page, scroll down to and click on the Your Devices section.
This will open a slightly more detailed list of recent sessions.
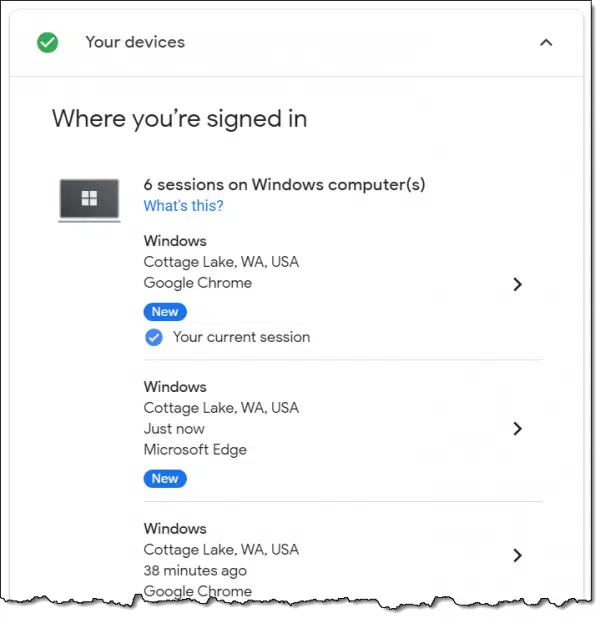
There may be enough additional information for you to recognize the usage behind the IP address. If not, click on the item representing that IP address and you’ll be given the option to sign that session out.
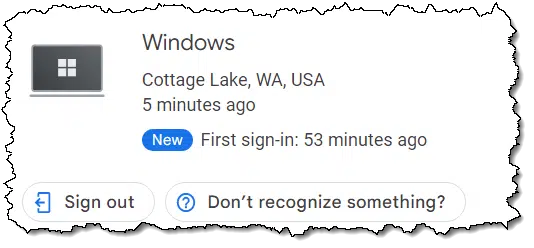
Click on Sign out to do so.
Now, immediately change your password.
Either of two things will happen:
- Unauthorized/unrecognized access will be terminated and cannot reconnect.
- Something you’re using — perhaps a program or service that you forgot was associated with your account — will stop working. It may take some time to realize this, but once you do, you’ll understand whether it’s something you want accessing your account, and you’ll recognize it in the future.1
Particularly when the access is from somewhere you don’t recognize, it might be time to consider further securing your account with two-factor authentication.
Do this
It’s worth having a look at account activity details when you’re not suspecting or experiencing a problem just to understand what “normal” looks like.
Then, particularly if you have reason to be suspicious or are concerned that your account is experiencing unauthorized access, take a look, and take action if warranted.
Another action to take: Subscribe to Confident Computing! Less frustration and more confidence, solutions, answers, and tips in your inbox every week.
Podcast audio
Footnotes & References
1: Interestingly, it’s possible that programs and services could appear as coming from other countries, depending on what you use. It’s safest to disconnect if you’re unsure.




once upon a time when you were signed in in more than one place there was a button that let you “sign out all other sessions”. for some reason that button is not there anymore.
I already have 2FA turned on for my Gmail (and outlook.com) account(s), but I went and looked anyway. There are several items listed, but they all (both current and recent activity) have the same IP address. This confirms that 2FA appears to be working so far, at least until some miscreant finds a way around it (or Google mucks up their security).
Ernie