Mysterious and hidden.

When you delete a file using Windows File Explorer, that file is placed in the Recycle Bin. The Recycle Bin in Windows has saved many a person from grief, I’m sure.
But where exactly is it, and do the deleted files still take up space?
Let’s look.

Recycle Bin space, location, and control
The Windows Recycle Bin stores deleted files, which take up space until the bin is emptied. Hidden on each drive, it can be managed by adjusting its size or deleting the folder entirely. It offers control over file recovery and space management across all drives and is accessible via a single desktop icon.
Where is it?
By default, the Recycle Bin is well hidden. It’s not enough, for example, to say “View Hidden Files” in Windows File Explorer settings. You must also UNcheck “Hide protected operating system files (Recommended)”.
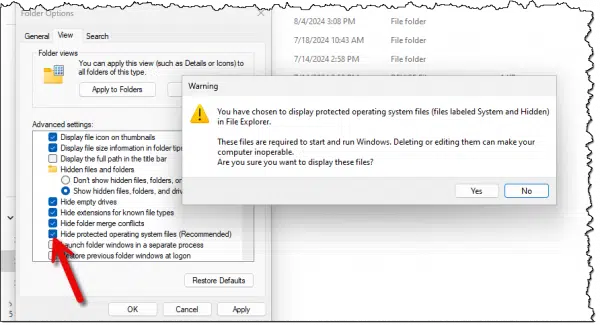
As you can see, before Windows respects your choice, it gives you a stern caution about the importance of those files.
Once you’ve clicked Yes, you’ll be able to see a Recycle Bin on all of your internal drives and most1 external drives. They have different names based on how the drive was formatted; on NTFS-formatted systems, it is named $Recycle.Bin. On FAT32/exFAT-formatted systems, it is named Recycle Bin.
In all cases, Recycle Bins are located in the root/top of the drive.
Note that the Recycle Bin may not exist until at least one file has been deleted.
Help keep it going by becoming a Patron.
How much space does it take up?
The Recycle Bin definitely takes up space. Since the “deleted” files aren’t really deleted at all, but instead moved to the Recycle Bin, they continue to take up space until the Recycle Bin is emptied or the file is deleted permanently.
However, you can control the upper limit of how much space the Recycle Bin can take up. Right-click on the desktop Recycle Bin icon and click on Properties.
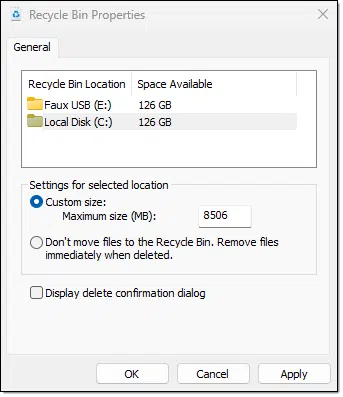
Each drive capable of having a Recycle Bin is listed, along with the size of the drive it’s on. Click on one of the drives, and you’ll be able to set the “Custom size” for the Recycle Bin on that drive. Once the Recycle Bin exceeds that size, older files will be removed — permanently deleted — to make room for newly recycled files.
Every drive, yet one control
Even though there are multiple Recycle Bin folders across multiple drives, there’s only one Recycle Bin icon on your desktop. Double-click it, and it will open in Windows File Explorer, listing all the files currently contained in all Recycle Bins.
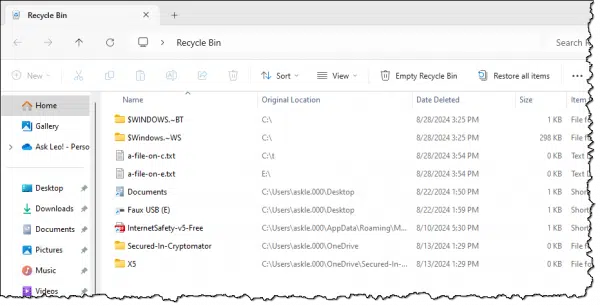
Note that the original location listed includes the drive on which the file is located. As per the toolbar items, you can Empty Recycle Bin to permanently delete all files in all Recycle Bin folders on all drives, or you can Restore all items to send all the files back to where they lived before you deleted them.
You can also right-click on a file and choose to Delete (meaning permanently delete) or Restore the individual file.
Emptying the Recycle Bin on only one drive
You may have multiple drives and multiple Recycle Bin folders (one per drive). What if you’re running low on space on only one of the drives and would like to empty the folder only on that drive?
There are two approaches.
In Recycle Bin properties, set the space to be used by that drive to 1MB (zero doesn’t work), click on Apply, and then reset the space to be used back to its original value.
That’s too cumbersome for me. I use a slightly different hack: I just delete the Recycle Bin folder on that specific drive. Surprisingly, the folder is not protected, and with “Hide protected operating system files” turned OFF, you can just click on it and delete it like any other folder. It and all its contents are permanently deleted. The next time you delete a file on that drive, it’ll be recreated.
Do this
The Recycle Bin is something we don’t think about often, but I can attest to its value. It’s saved my bacon on more than one occasion.
And now you have a little more understanding of where it is and how it works.
Subscribe to Confident Computing! Less frustration and more confidence, solutions, answers, and tips in your inbox every week.
Podcast audio
Footnotes & References
1: Thumbdrives generally do not have Recycle Bins, but larger external drives typically do.



Holding down the shift key when deleting a file will bypass the recycle bin and permanently delete it (still recoverable with a file recovery program if you catch it soon enough). So be careful doing this.
Why Aren’t Deleted Files Always Moved into the Recycle Bin?
I Deleted a File by Mistake. Can I Get It Back?
Hi Leo
The recycle bin in Windows 11 appears on the home page of my
desktop and everything I delete is shown there.
So could you tell us what the other recycle bins contain that you
mentioned and also I would feel concerned at unchecking the box
and ignoring Microsoft’s warning.
Thank you
Allan
The other recycle bins are the recycle bins on the other drives or partitions. The Recycle Bin on the desktop is a composite view of all the individual recycle bins.
Leo, you wrote:
“Thumbdrives generally do not have Recycle Bins…”
Is there any way of forcing the creation of a Recycle Bin on a Flashdrive? (Not that I’d ever want to — I find the Recycle Bin to be a nuisance, myself — but the knowledge might be useful to others, or perhaps to myself under other circumatances)…
It can be done There are a few ways. You can do a web search to find one.
I’m told there may be third party tools, but I’d not recommend it. Certainly nothing I’ve ever tried myself.
Can I add other ‘drives’ to the recycle bin shown on my desktop?
Specifically I have an NAS, and have mapped 4 folders on the NAS as drives on my personal PC. Logging onto the NAS to inspect and empty the several recycle bins there is cumbersome. I would rather be able to inspect the Recycle of Bin of say my “M:” drive (Deleted Macrium backups in this case) directly from my desktop. Files on those mapped drives do not currently show in my PC’s reycle bin.
Not that I’m aware of. Networked devices need to remain separate, I believe, because they can come and go.
One feature I wish the recycle bin had was the ability to show the preview (Alt+P) panel, More than once I have opened the recycle bin to recover an image file where the file name alone was insufficient to identify the desired image.
Try opening the recycle bin, then look on the upper right-hand side.
There you should find the word ‘details’. Click on that.
Now hover over any deleted file and you will find full details of that file.
I have just deleted 27 photos and each image is shown, with details, when I hover the cursor over the file.
I am using Windows 11 and I regularly check specific items before emptying the bin.
Hope it works for you.
Whenever I ‘delete’ a file in Windows, I open the recycle Bin and check out what’s in there, and since there’s usually nothing I need, or didn’t expect to find there (at least since I got rid of OneDrive), I click the ‘Empty Recycle Bin item in the ribbon menu at the top of the window. While I know I can Alt-Click the trash can on my desktop, then click the “Empty Recycle Bin” item in the context menu, I prefer to open it’s window so I can see everything in there before I empty it. On a few occasions I’ve inadvertently deleted nearly irreplaceable files, only to discover my mistake too long after the deletion for file recovery utilities to be of any use, so now I open the Recycle Bin’s window before deleting anything to prevent that ever happening again, at least as much as I can.
Ernie
I think you mean right-click the Recycle bin icon which gives a menu that allows you to empty it.
No, I click the Recycle Bin icon on my desktop to open it in Windows Explorer so I can see the list of what I’m deleting before I do so.
I’m referring to where you said “While I know I can Alt-Click the trash can on my desktop,”
Alt-Clicking the trash can icon does nothing. I think you mean double-click the Trash Icon. That’s what confused me.
Leo:
In your recommendation to delete the Recycle Bin folder in specific drives (other than C drive), how does one know that there is nothing critical in that folder that will be deleted?
The Recycle Bin doesn’t hold critical data (unless you delete something critical 😉 ). Clearing it the normal way deletes all the same things except for a couple of hidden system files which are immediately recreated after deletion.